Creation of a low-cost, battery-operated tool used during both the Ebola and COVID-19 responses that manages the flow rate of IV treatments with a simple gravity system, replacing the need for expensive, difficult-to-use infusion pumps.
Global Health R&D across the US government | USAID
Global Health R&D at the US Agency for International Development
 What does USAID do for global health R&D?
What does USAID do for global health R&D?
The US Agency for International Development (USAID) supports the development, introduction, and scale-up of urgently needed drugs, vaccines, and other technologies to address unmet health needs of people in the world’s poorest places. The agency specializes in late-stage clinical research and implementation research and operates Grand Challenges to identify and advance promising health innovations from around the world.
 Why is USAID’s role in global health R&D important?
Why is USAID’s role in global health R&D important?
USAID is the only US agency with a mandate to focus on global health and development, which means it is uniquely positioned to support product development and innovation to advance global health. The agency’s deep international footprint, combined with its in-depth understanding of community needs and culture, makes it critical for developing new health tools that are appropriate, affordable, and accessible for widespread uptake in low-resource settings.
 USAID support is advancing:
USAID support is advancing:
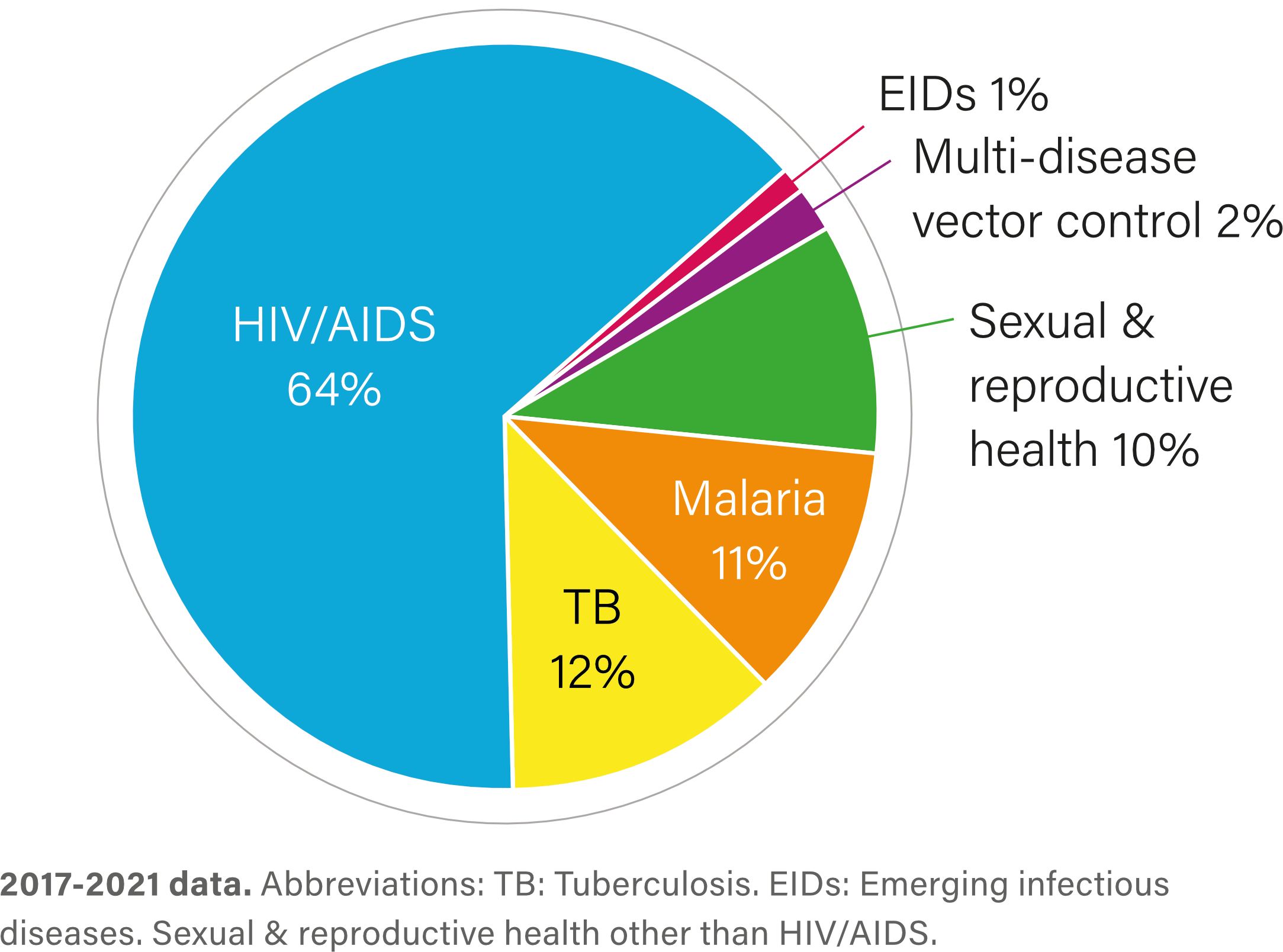
 R&D investment by health area
R&D investment by health area
IMPACT OF INVESTMENT
GLOBAL HEALTH SECURITY
HIV/AIDS
Development of a woman-controlled microbicide vaginal ring, the first long-acting HIV prevention method to receive a positive regulatory opinion.
MALARIA
Development of a child-friendly malaria medicine, which has been distributed in more than 50 nations and has saved an estimated 960,000 child lives since its introduction in 2009.
TB
Development of child-friendly tuberculosis (TB) medicines, which have been adopted in 123 countries that collectively account for more than 75 percent of the global childhood TB burden.
NEWBORN HEALTH
Adaptation of the antiseptic chlorhexidine for umbilical cord care, which is projected to save the lives of more than 1 million babies by 2030 at a cost of less than US$.50 per dose.
MENINGITIS
Development of a low-cost meningitis A vaccine, which as of 2020, has been delivered to more than 340 million people in 24 countries, virtually eliminating meningitis A wherever it has been used.
